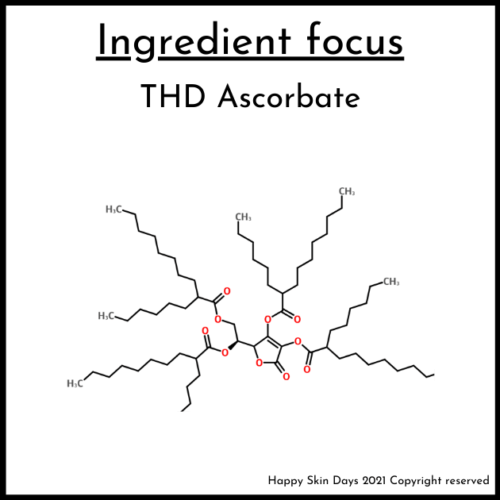
In today’s blog, I am doing a deep-dive into Tetrahexyldecyl Ascorbate (THD Ascorbate). I have also seen it referred to as tetra-isopalmitoyl ascorbic acid, but its official (INCI name) is THD Ascorbate. But before that….
My view on THD Ascorbate

1) Chemical structure
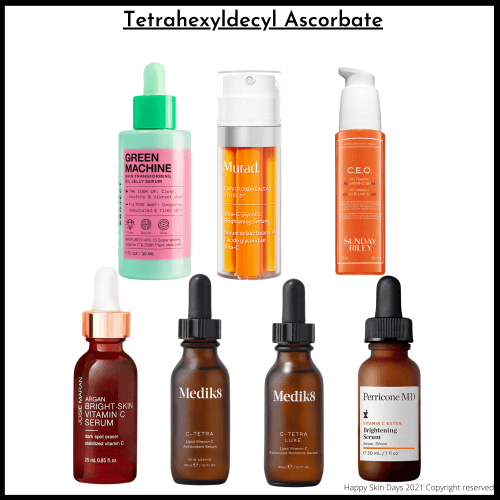
2) Products containing THD Ascorbate


3) What characteristics of Vitamin C (L-Ascorbic Acid) do we want THD Ascorbate to replicate?
“The chemically active form of the ascorbic acid used in medical practice is L-ascorbic acid (LAA) (Ravetti et al).” This compound achieves the following:
- its essential for the synthesis of new collagen in the dermis. Topical application of L-Ascorbic Acid has been demonstrated to produce new collagen in the dermis
- it is a skin lightener, as it interferes with the enzymatic activity of tyrosinase, an enzyme that is vital for the production of the pigment (melanin) that in turn, gives skin its colour
- is a potent anti-oxidant and has been demonstrated to reduce reactive oxygen species on exposure to UV radiation as well as reduce subsequent photodamage.
4) How does THD Ascorbate stack-up?
There is no doubt that THD Ascorbate is a skin-lightener. In Japan, THD Ascorbate is regulated as a quasi-drug and its permitted to 3%. To achieve this quasi-drug status, data demonstrating THD Ascorbate’s efficacy as a skin-whitener, has to have been demonstrated to a government agency.
Also, like all Vitamin C derivatives, its a potent anti-oxidant reducing Reactive Oxygen Species.
I am not persuaded about THD Ascorbate’s efficacy in producing collagen (and you’ll see why below).
5) What studies/clinical trials have I found?
Patricia M.B. et al have demonstrated that THD is a stable derivative of Vitamin C, that also has, “pronounced moisturising effects on (the) stratum corneum and viable epidermis.”
Ochiai Y et al in a clinical study have shown that THD Ascorbate:
- is a Vitamin C precursor
- effectively, reduces
reduces UVB induced skin-pigmentation, likely by suppressing ROS. Therefore, its also a potent anti-oxidant.
What’s also interesting is that looks as if it also protects against UVA induced oxidative stress, which really is the crux of photodamaged skin (Source: Xiao L et al).
Fitzpatrick et al, tested a newly formulated Vitamin C complex containing 10% LAA (water soluble) and 7% THD ascorbate (lipid soluble) was applied to one half of the face of 10 subjects in a double blind study. There was a statistically significant improvement on the vitamin C-treated side. This was demonstrated by an i improvement in wrinkles after 12 weeks of topical use. Fitzpatrick et al, concluded that this clinical improvement related to biopsy evidence of new collagen formation.
(My view: its anyone’s guess as to whether the LAA caused the collagen formation or the 7% THD Ascorbate. Again this was a limited study because only 10 participants (see below).
The final clinical trial I found,
tested the tolerance parameter of Vitamin C (30% THD Ascorbate) and 0.5% retinol on 44 women with mild to moderate hyperpigmentation and photodamaged facial skin over a 12 week period.
Unfortunately, no measurements of change in photodamage, skin lightening or new collagen synthesis was made. The study was limited to testing tolerance of skin to such an aggressive skincare routine. (And yes, dryness was one of the parameters that the researchers were looking for).
6) What do manufacturers suggest?
I looked up a paid-subscription service, Ultroprospector and there are multiple manufacturers of THD Ascorbate.
This pdf is from MakingCosmetics website and is publicly available

This blog was last updated on 4 August 2021 and unless otherwise stated, it will not be updated again.
Sources and uses
Xiao L et al Cytoprotective effects of the lipoidic-liquiform pro-vitamin C tetra-isopalmitoyl-ascorbate (VC-IP) against ultraviolet-A ray-induced injuries in human skin cells together with collagen retention, MMP inhibition and p53 gene repression. J Cell Biochem. 2009 Mar 1;106(4):589-98
Ochiai Y et al A new lipophilic pro-vitamin C, tetra-isopalmitoyl ascorbic acid (VC-IP), prevents UV-induced skin pigmentation through its anti-oxidative properties. J Dermatol Sci. 2006 Oct;44(1):37-44.
Patrícia M.B.G. et al Application of tetra-isopalmitoyl ascorbic acid in cosmetic formulations: Stability studies and in vivo efficacy, European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics, Volume 82, Issue 3
Herndon, J. H. et al An open label clinical trial to evaluate the efficacy and tolerance of a retinol and vitamin C facial regimen in women with mild-to-moderate hyperpigmentation and photodamaged facial skin. J.Drugs Dermatol. 2016;15(4):476-482.
Fitzpatrick, R. E. et al Double-blind, half-face study comparing topical vitamin C and vehicle for rejuvenation of photodamage. Dermatol.Surg. 2002;28(3):231-236.
Safety Assessment of Ethers and Esters of Ascorbic Acid as Used in Cosmetics (2017) by the Cosmetic Ingredient Review
Ando et al Quasi-Drugs Developed in Japan for the Prevention or Treatment of Hyperpigmentary Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 2566–2575