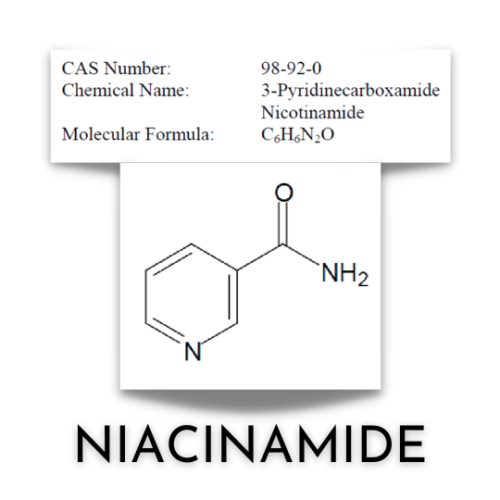
As indicated in an earlier blog, I am on a mini-mission to find out everything about Niacinamide.
In today’s blog, I am looking at background information about Niacinamide (rather than skin specific issues)
Niacinamide as a vitamin
I hope everyone reading this blog understands that vitamins are essential nutrients for the functioning of the body.
If this is a revelation and it stuns you, then this is not the blog for you. Sorry.
Vitamins are fat-soluble and water-soluble. Vitamins C and the B group of vitamins are water-soluble which means they are not being stored in our bodies and there has to be a continuous process of replenishing them.
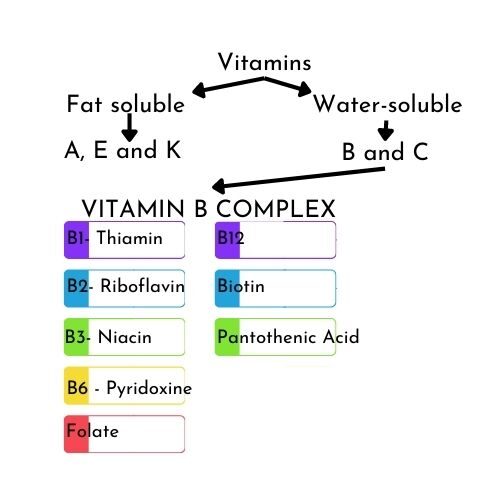
I have shown 8 groups of vitamins and these are found in foods such as cereal grains, meat, poultry, eggs, fish, milk, legumes and fresh vegetables (source: Fact Sheet no 9.312 below)
B-complex vitamins
I will briefly highlight what each of the B vitamins are but our main interest is Vitamin B3 – Niacin.
B-Vitamins are essentially co-enzymes and they are deeply integral to the process of getting energy from food for our body
According to Fact Sheet no 9.312
- Thiamin (Vitamin B1): helps release energy from food, promotes normal appetite and important to maintaining proper nervous system
- Riboflavin (Vitamin B2): helps release energy from food, promotes good vision + healthy skin
- Niacin (Vitamin B3): involved in energy production, normal enzyme function, digestion, promoting normal appetite, healthy skin and nerves
- Pyridoxine (Vitamin B6): aids in protein metabolism and red blood cell formation. Involved in production of important chemicals such as haemoglobin and insulin in our body
- Folate (Folic Acid): aids in protein metabolism, promotes red blood cell formation and lowers the risk for neural tube birth defects.
- Cobalamin (Vitamin B12): aids in building of genetic material, production of normal RBS and maintenance of nervous system
- Biotin: helps release energy from carboyhdrates and aids in metabolism of fats, proteins and carbohydrates
- Pantothenic Acid: necessary for energy production and aids in formation of hormones and metabolism of fats, proteins and carbohydrates from food
What is Niacinamide
Niacinamide is the active form of the Vitamin Niacin.
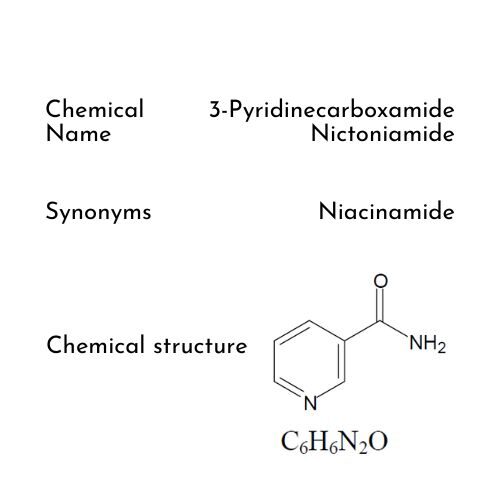
Niacinamide is an essential component of the coenzyme NAD, which is involved in energy production.
The short form is as follows:
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) is not only a coenzyme for oxidoreductases but also serves as a substrate for three classes of enzymes: sirtuin family deacetylases (SIRT1-7), poly(ADP)-ribosyl polymerases (PARP1-2), and cADP-ribose synthases (CD38 and CD157) (22, 66). NAD+ can be reduced to NADH via dehydrogenases and can also be phosphorylated to NADP+ via NAD+ kinases (NADKs). The NAD+/NADH redox couple is known as a regulator of cellular energy metabolism, that is, of glycolysis and mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation. By contrast, NADP+ together with its reduced form, reduced NADPH, is involved in maintaining redox balance and supporting the biosynthesis of fatty acids and nucleic acids (141, 144). Given the crucial roles of NAD+/NADH and NADP+/NADPH in regulating the cellular redox state, energy metabolism, mitochondrial function, gene expression, and signaling pathways, these redox couples are essential for maintaining a large array of biological processes (22, 24, 144). Thus, loss of redox homeostasis of these molecules has been linked to a variety of pathological conditions, such as cardiovascular diseases, neurodegenerative diseases, cancer, and aging (24, 144).
Xiao W, Wang RS, Handy DE, Loscalzo J. NAD(H) and NADP(H) Redox Couples and Cellular Energy Metabolism. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2018 Jan 20;28(3):251-272. doi: 10.1089/ars.2017.7216. Epub 2017 Jul 28. PMID: 28648096; PMCID: PMC5737637.
What should I take away from this blog?
Niacinamide as a co-enzyme is essential to these functions at a cellular level in the body:
- Cellular Redox State
- Energy Metabolism
- Mitochondrial Function
- Gene Expression
- Signalling Pathways
See also
Sources and uses
This blog relies heavily on this document, which in many parts is produced verbatim: Colorado State University Food and Nutrition Series/Health Fact Sheet No. 9.312
OECD SIDS 3-Pyridine Carboxamide (Nicotinamide) CAS No 98-92-0
Xiao W, Wang RS, Handy DE, Loscalzo J. NAD(H) and NADP(H) Redox Couples and Cellular Energy Metabolism. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2018 Jan 20;28(3):251-272. doi: 10.1089/ars.2017.7216. Epub 2017 Jul 28. PMID: 28648096; PMCID: PMC5737637.